Microblog starter + Astro
#Overview
Use our Microblog starter with Astro to create a microblog.
#Quickstart: Clone the Astro microblog starter
Let's get into a simple example of connecting the Astro framework with Hygraph using the microblog starter from the marketplace:
Or you can clone the Astro microblog by typing the following command in your terminal:
npx degit git@github.com:hygraph/hygraph-astro-microblog-starter.git
Navigate to the project directory and type npm install to install the package dependencies by typing the following command:
cd hygraph-astro-microblog-starter && npm install
Once the installation process is finished, create a .env file in the root directory and the ASTRO_HYGRAPH_ENDPOINT variable with a link to your API endpoint from Hygraph.
Run the command npm run dev and your microblog will be available in the browser via localhost:
 Astro - localhost
Astro - localhost
Your assigned localhost port number may vary depending on your environment, but the assigned port and the link will be available to you in the terminal.
Your microblog is now available locally via localhost at http://localhost:NUMBER-IN-YOUR-TERMINAL!
 Astro - microblog
Astro - microblog
#Code overview
Now that we have our Hygraph project and Astro frontend up and running, let's take a quick dive into the code of the starter.
Hygraph endpoint GraphQL queries for posts
The fragments directory in your Astro code contains two GraphQL fragments:
export const postsFragment = `pageInfo {hasNextPageendCursor}postsArray: edges {cursorpost: node {slugidcreatedAtcontent {html}}}`;export const postFragment = `idslugcontent {html}createdAt`;
The postsFragment is used to fetch information about a list of posts to implement the lazy load pagination feature of the microblog.
The postFragment is used to fetch information about each post to render on individual pages.
Individual post pages
To create the individual blog post pages, we are using the getStaticPaths function, an Astro helper function that's used to generate static paths for each blog post.
This function fetches data from a GraphQL endpoint (specified by ASTRO_HYGRAPH_ENDPOINT environment variable) using a POST request. The request body contains a GraphQL query that fetches posts using the postFragment:
---import Main from "../../layouts/Main.astro";import Post from "../../components/Post.astro";import { postFragment } from "../../../fragments/posts";//export getstaticpathsexport async function getStaticPaths() {const response = await fetch(import.meta.env.ASTRO_HYGRAPH_ENDPOINT,{method: "POST",headers: {"Content-Type": "application/json",Accept: "application/json",},body: JSON.stringify({query: `query MyQuery() {posts() {${postFragment}}}`,}),});const json = await response.json();const paths = json.data.posts.map((post) => ({params: { slug: post.slug },props: { post },}));return paths;}const {post} = Astro.props---<Main title="My Microblog"><div><Post post={post} /></div></Main>
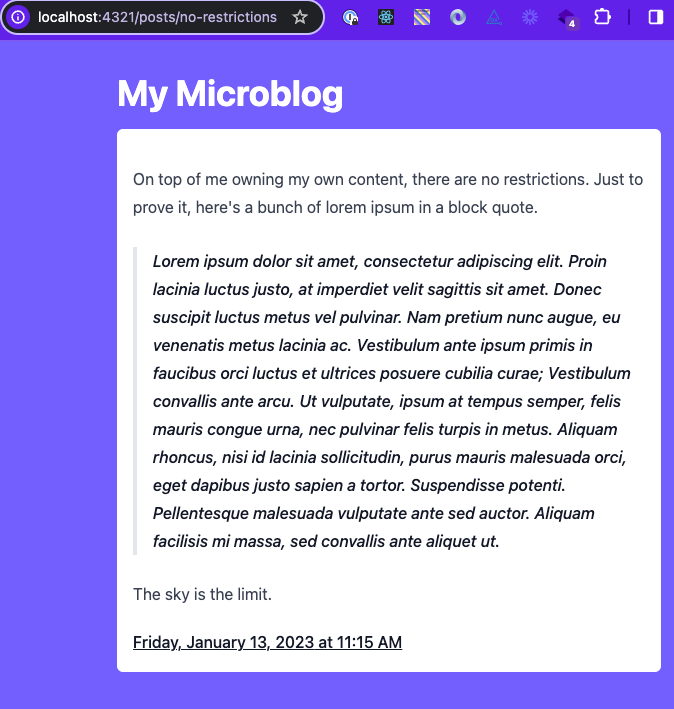
The above code generates individual post pages with their respective content:
 Astro - individual post pages
Astro - individual post pages
Individual post pages will contribute to a more organized, engaging, and user-friendly microblog.
For more Astro implementations, check out our Astro Skncre starter!